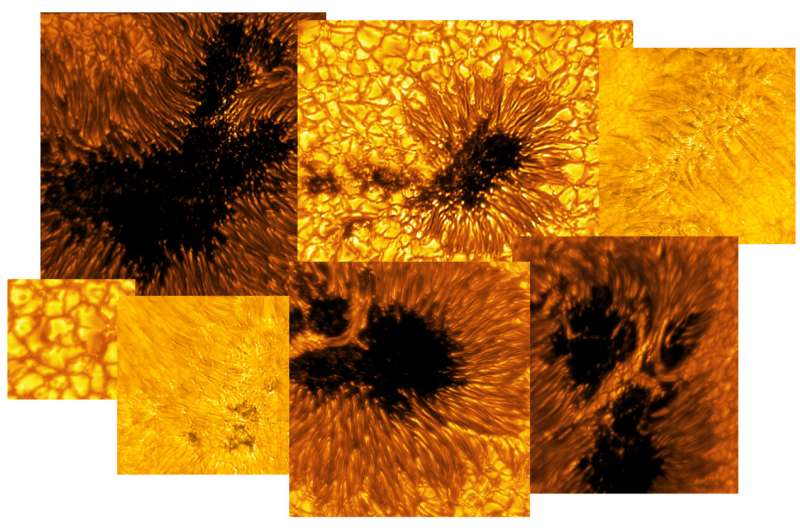
The National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope released eight new images of the sun, previewing the exciting science underway at the world’s most powerful ground-based solar telescope. The images feature a variety of sunspots and quiet regions of the sun obtained by the Visible-Broadband Imager (VBI), one of the telescope’s first-generation instruments.
The Inouye Solar Telescope’s unique ability to capture data in unprecedented detail will help solar scientists better understand the sun’s magnetic field and drivers behind solar storms.
The sunspots pictured are dark and cool regions on the sun’s “surface”, known as the photosphere, where strong magnetic fields persist. sunspots vary in size, but many are often the size of Earth, if not larger. Complex sunspots or groups of sunspots can be the source of explosive events like flares and coronal mass ejections that generate solar storms. These energetic and eruptive phenomena influence the outermost atmospheric layer of the sun, the heliosphere, with the potential to impact Earth and our critical infrastructure.
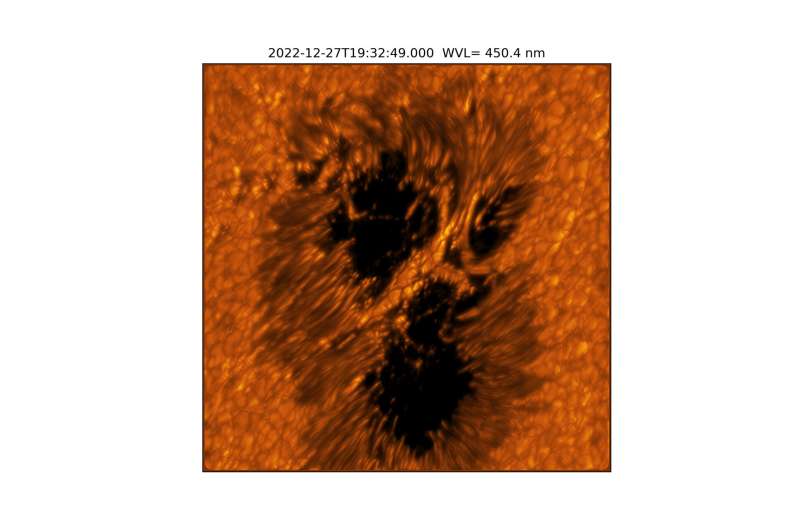
In the quiet regions of the sun, the images show convection cells in the photosphere displaying a bright pattern of hot, upward-flowing plasma (granules) surrounded by darker lanes of cooler, down-flowing solar plasma. In the atmospheric layer above the photosphere, called the chromosphere, we see dark, elongated fibrils originating from locations of small-scale magnetic field accumulations.
The recently inaugurated telescope is in its Operations Commissioning Phase (OCP), a learning and transitioning period during which the observatory is slowly brought up to its full operational capabilities.
The international science community was invited to participate in this phase through an Operations Commissioning Phase Proposal Call. In response to these calls, investigators submitted science proposals requesting telescope time for a specific and detailed science goal. In order to optimize for science return, while balancing the available observing time and the technical needs in this very early operational phase, the proposals were subsequently peer-reviewed by a proposal review committee and telescope time was granted by a Telescope Allocation Committee. The selected proposals were executed in 2022 during the Cycle 1 operations window.
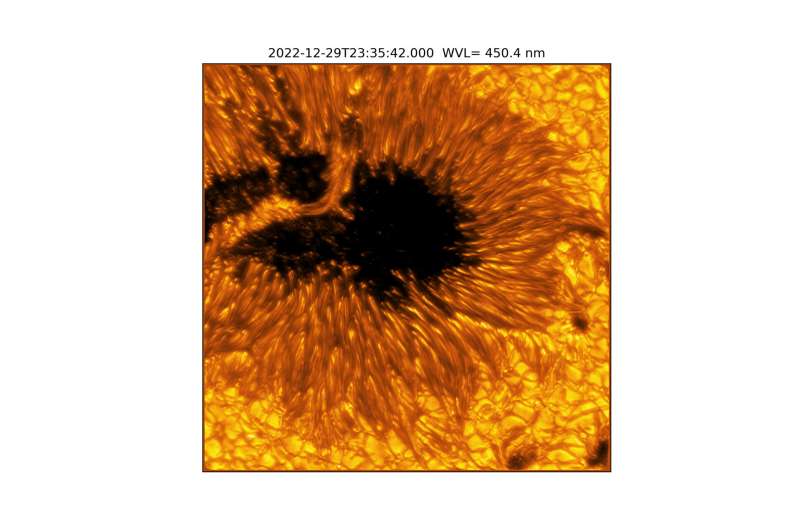
The newly released images make up a small fraction of the data obtained from the first Cycle. The Inouye Solar Telescope’s Data Center continues to calibrate and deliver data to the scientists and public.
As the Inouye Solar Telescope continues to explore the sun, we expect more new and exciting results from the scientific community—including spectacular views of our solar system’s most influential celestial body.
Provided by
Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy
Citation:
New images released by Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (2023, May 19)
retrieved 19 May 2023
from
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
 Innovation Discoveries Latest Scientific Discoveries in Innovation
Innovation Discoveries Latest Scientific Discoveries in Innovation



